

La plataforma importa: diseño único de tejido entrelazado del Stent Supera™
Tecnología revolucionaria en la plataforma del Stent
Fuerza - su alta resistencia a la compresión1
Baja fuerza crónica hacia afuera contra las paredes de los vasos2
Alta flexibilidad,3 lo que permite la resistencia a la fractura4
Ver la diferencia del Stent Supera™
El diseño de nitinol entrelazado proporciona una alta integridad estructural y resistencia a las torceduras, produciendo las características que distinguen al stent Supera™.
Ofrece una fuerza para la resistencia a la compresión
El stent Supera™ exhibe más de 4 veces la resistencia a la compresión de todos los demás stents de nitinol autoexpandibles.2
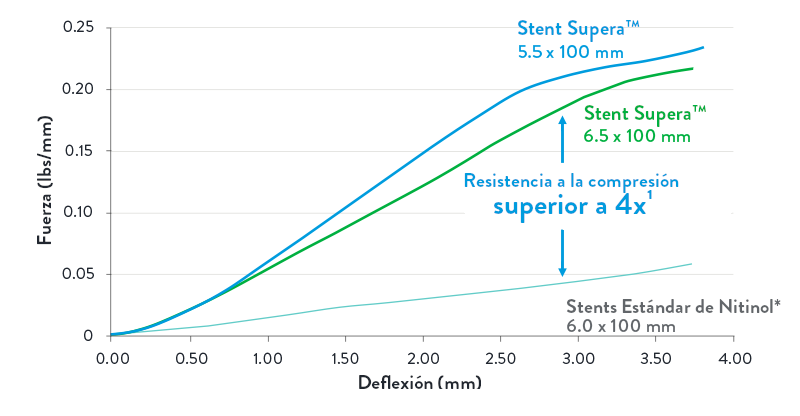
Optimiza la ganancia luminal y mantiene la geometría circular
SUPERA™ STENT21
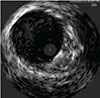
La misma arteria mostrada, Stent Estándard de Nitinol.
SNS21
Ejercer la menor fuerza crónica hacia afuera sobre la pared del vaso2
Si bien los stents de nitinol cortados con láser están diseñados y deben ser de gran tamaño para su implementación, el stent Supera™ es único en el sentido de que tiene un tamaño de 1:1 con el diámetro del vaso. Como se ve en la imagen a continuación, los stents cortados con láser ejercen inherentemente fuerza sobre la pared del vaso durante toda la vida útil del stent, lo que a su vez puede resultar en lesiones endovasculares a largo plazo. La menor fuerza crónica hacia afuera (COF) con el stent Supera™ da como resultado menos lesiones vasculares.2,4
Diseños de stents estándar de nitinol (SNS)
 |
Empuja contra la pared del vaso para abrirse, a lo largo de la vida útil del SNS |  |
 |
|
SOBREDIMENSIONAMIENTO
DEL STENT
|
ALTO COF2 | LESIÓN DEL VASO4 | |
| La fuerza crónica hacia afuera (COF) se ejerce sobre el vaso mediante stents autoexpandibles debido al sobredimensionamiento inherente | |||
Stent Supera™
 |
El tamaño 1:1 permite soportar la pared del vaso para mantenerlo abierto |  |
 |
| TAMAÑO 1:1 | COF BAJO2 | LESIÓN MÍNIMA DEL VASOY4 |
|
| El stent Supera™ tiene un tamaño de 1:1 con el vaso preparado y, por lo tanto, tiene una fuerza crónica mínima hacia afuera | |||
Proporcionando una flexibilidad sin precedentes3 y Cero Fracturas4-20
Otros stents de nitinol autoexpandibles se fabrican a partir de un tubo rígido e inflexible que se corta con láser. Como se muestra en la foto a continuación, debido al diseño y las propiedades de los materiales, es menos probable que algunos stents cortados con láser se adapten a un entorno vascular dinámico, pueden doblarse y fracturarse en vasos tortuosos (izquierda).
Stent cortado con láser

Stent Supera™

Sin embargo, con el Stent Supera™, los alambres flexibles individuales de nitinol se entrelazan para una flexibilidad sin precedentes,3 excelente resistencia a las torceduras y la capacidad de imitar el movimiento natural de la anatomía1,21,22 (derecha).
En consecuencia, los datos de más de 2.000 pacientes publicados en 17 estudios han demostrado que al año el stent Supera™ tiene cero fracturas.4-20


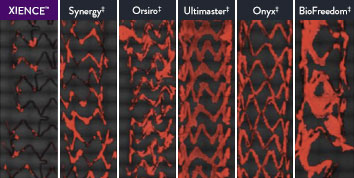
The XIENCE™ Stent is also recognized as being significantly more anti-thrombotic than other DES on the market. As shown in the study findings, XIENCE™ Stent reveals significantly less (p < 0.01) platelet adhesion—shown in red in the confocal microscopy images—than other DES, and platelet adhesion is an important factor in stent thrombosis.*8 These findings suggest that this stent choice “may be ideally suited for very short-term DAPT.”8
*Ex Vivo Swine Shunt Model.

Diamondback 360™ OAS Gives You the Versatility to Treat Challenging Cases
Treat even the most severely calcified lesions, with under 2-minute setup7,8 and predictable procedure times.2
Facilitates antegrade and retrograde treatment of:
- Long, Diffuse Lesions
Successfully treated lesions up to 60 mm in length in real-world study.9 - Heavily Stenosed Lesions
Crossed >99% of lesions with <2% pre-dilatation in the ORBIT II study.1,10 - Nodular Lesions
Effectively treats nodular calcification.5,6 - Ostial Lesions
Safely treats ostial lesions.11-13
Low Profile
6F compatible for femoral or radial access.14
Multiple Vessel Sizes
A single 1.25 mm crown treats vessels 2.5 mm to 4.0mm14
|
|
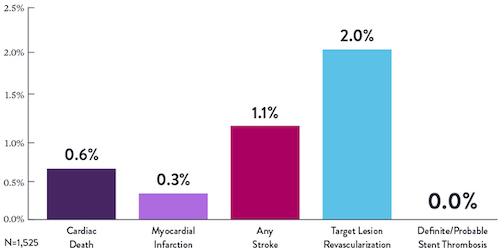
Proven Safety |
Procedural Success |
Low Q-Wave MI Rate |
>2,200 |
<1% |
97.7% |
0.9% |
|
Patients Across 11 |
Component Angiographic |
Crossing and Stent |
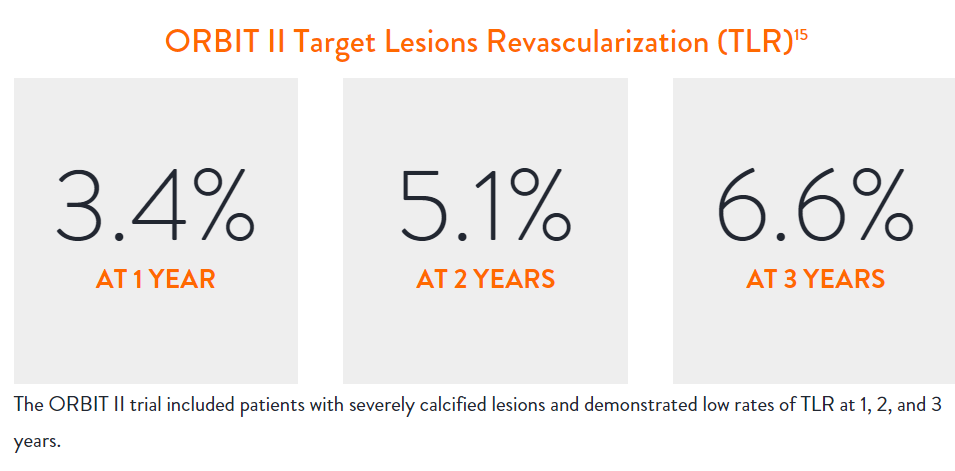
In the ORBIT II |
Sustained Clinical Performance
Data are for ORBIT II TLR in the OA+DES patient cohort.

“Stopping DAPT at 3 months in selected patients after [XIENCE™ Stent] implantation was at least as safe as the prolonged DAPT regimen adopted in the historical control group.”
— Masahiro Natsuaki, MD, STOPDAPT Trial9

STOPDAPT 2 Trial Design and Randomization10

Short 1-Month DAPT
- 0 to 1-month: Aspirin + P2Y12
- After 1-month: Clopidogrel monotherapy

12-Month DAPT
- 0 to 1-month: Aspirin + P2Y12
- 1 to 12-month: Aspirin + Clopidogrel
- 12 to 60-month: Aspirin monotherapy

- Successful PCI using CoCr everolimus-eluting stent: XIENCE™
- Eligible for DAPT (aspirin/P2Y12 receptor blocker) for 1 year

- Patients who need oral anticoagulants
- History of intracranial bleeding
- Major in-hospital complications (MI/stroke/major bleeding)
STOPDAPT Study: XIENCE™ Stent with 3-Month DAPT Is Feasible9
STOPDAPT9 was the first prospective trial to study DAPT cessation at 3 months after implantation. Among other 1-year outcomes, the XIENCE™ Stent rate of stent thrombosis was 0.0%.
STOPDAPT Study Demonstrates Feasibility of XIENCE™ Stent with 3-Month DAPT9

Learn more about STOPDAPT 2

“It was noteworthy that no definite or probable stent thrombosis occurred in [XIENCE™ Stent] patients enrolled in STOPDAPT.”
— Masahiro Natsuaki, MD, STOPDAPT Trial9

STOPDAPT-3 Trial Design and Randomization11

- PCI with planned exclusive use of CoCr-EES (XIENCE)
- ACS presentation or ARC-HBR
- Eligible for DAPT (Aspirin/P2Y12inhibitor) for 1 month
Study design and Randomization
Group 1:
0 to 1-month: Aspirin + P2Y12 (Prasugrel)
After 1-month: Clopidogrel monotherapy
Group 2:
0 to 1-month: P2Y12 (Prasugrel)
After 1-month: Clopidogrel monotherapy
STOPDAPT-3 Trial 11 was designed to explore 0-month DAPT* (SAPT˄ using only P2Y12 inhibitor) for ACS and HBR patients.
Though the results are comparable for both bleeding and ischemic events for DAPT and SAPT arms, the study did not meet its endpoint and concluded to use DAPT for 1 month after PCI.
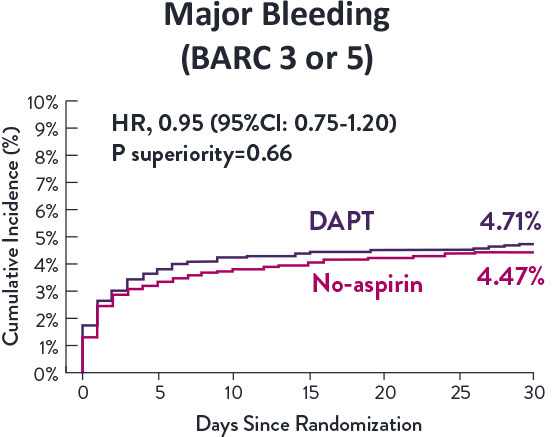
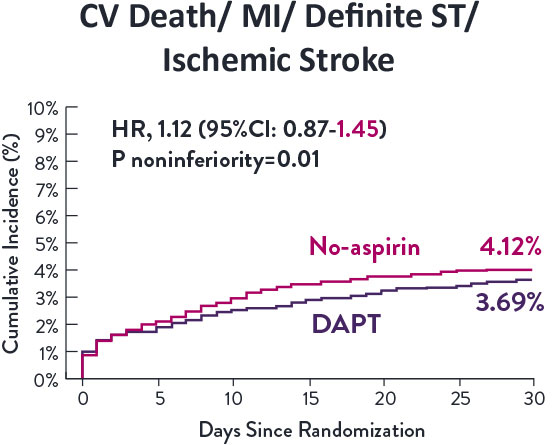
XIENCE™ Stent remains the ONLY DES with the shortest DAPT indication, as short as 28 days.12


Referencias
- Data on file at Abbott.
- Competitors tested include Astron Pulsar-18, Complete SE, EverFlex, Innova, LifeStent, Misago, S.M.A.R.T., and Zilver PTX. Data on file at Abbott.
- Flexibility is defined as kink resistance. Competitors tested include Astron Pulsar-18, Complete SE, EverFlex, Innova, LifeStent, Misago, S.M.A.R.T., and Zilver PTX. Data on file at Abbott.
- Garcia L. et al., Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2017 Jun 1;89(7):1259-1267.
- Brescia AA. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2015 Jun;61(6):1472-8
- Chan YC. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2015 Nov;62(5):1201-9.
- Dumantepe M. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2017 Jul;51(5):240-246.
- George JC. et al., J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014 Jun;25(6):954-61.
- Goltz JP. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2012 Jun;19(3):450-6.
- León LR Jr. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2013 Apr;57(4):1014-22.
- Montero-Baker M. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2016 Oct;64(4):1002-8.
- Myint M. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2016 Jun;23(3):433-41.
- Palena LM. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2018 Oct;25(5):588-591.
- Scheinert D. et al., JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Jan;6(1):65-71.
- Scheinert D. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2011 Dec;18(6):745-52.
- Steiner S. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2016 Apr;23(2):347-55.
- Werner M. et al., EuroIntervention. 2014 Nov;10(7):861-8.
- San Norberto EM. et al., Ann Vasc Surg. 2017 May;41:186-195.
- Teymen B. et al., Vascular. 2018 Feb;26(1):54-61.
- Bhatt H. et al., Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2018 Jul;19(5 Pt A):512-515.
- Arena F. et al., J Vasc Med Surg. 2013:1;116.
- Chen Y. et al., J Vasc Surg 2014;59:384-91.

MAT-XXXXXXX



