

Stent Periférico Supera™
El Stent Periférico Supera™ es una clase única de tecnología AFS. Diseñado con una innovadora tecnología de alambre entrelazado, este stent de nitinol ofrece a los médicos resultados clínicos inigualables1-12 en diversas complejidades de lesiones y longitudes.1, 13-15
Los resultados importan
El Stent Supera™ es conocido por la excelencia de sus resultados clínicos después de los procedimientos de angioplastia transluminal percutánea (ATP) con colocación de stent, ya que este stent periférico se ha estudiado en más de 2.000 pacientes y 17 estudios en todo el mundo.1,15-30
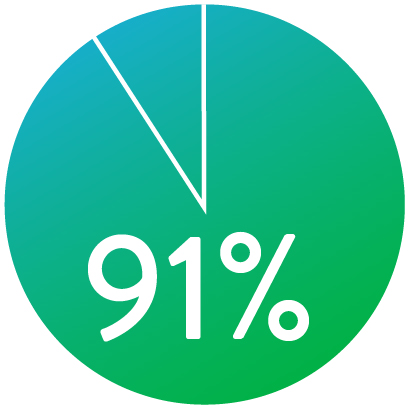
PERMEABILIDAD (K-M) A 1 AÑO
Cuando se despliega nominalmente*
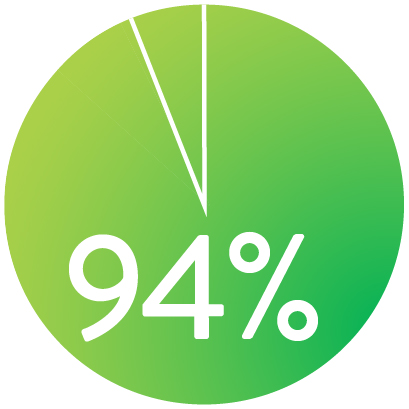
LIBERTAD DE TLR A LOS 3 AÑOS
Cuando se despliega nominalmente*
*El despliegue nominal se define como la longitud del stent en el momento del despliegue que se encuentra dentro de +/- 10% de la longitud del stent. Estos datos provienen de un análisis post-hoc no potenciado.
Demuestra excelentes resultados clínicos
El Stent Supera™ demostró una excelente permeabilidad de 1 año y 3 años de ausencia de TLR en la prueba SUPERB.1
1
Resultados clínicos notables
Resultados clínicos inigualables demostrados en lesiones simples1-12
2
Permeabilidad constante independientemente de la longitud de la lesión*
Exhibe resultados consistentes de permeabilidad primaria a 1 año, independientemente de la longitud de la lesión13-20,31
3
Resultados sólidos en la calcificación
Revela resultados clínicos sólidos en lesiones severamente calcificadas a 1 año y 3 años1
El estudio reportó un 93,8% de lesiones A y B del Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus Document (TASC) y/o lesiones de clase 2 o 3 de Rutherford
*Las tasas de permeabilidad se han evaluado en estudios con longitudes de lesión que oscilan entre 5,3 cm y 28,0 cm.
La plataforma importa
A diferencia de cualquier otra plataforma de diseño de stent, el Stent Supera™ está diseñado de manera única para mantener los vasos abiertos con su plataforma distintiva, creada por alambres de nitinol individuales y flexibles entrelazados.
Alta resistencia a la compresión32
4 veces más fuerza para la resistencia a la compresión, por lo que puede mantener un lumen redondo y abierto, lo que puede ser especialmente beneficioso en lesiones calcificadas
![]()
Baja fuerza crónica hacia afuera32
Con un tamaño 1:1 del stent al vaso, la baja fuerza crónica hacia afuera da como resultado una lesión mínima del vaso34
![]()
Alta Flexibilidad33 y Resistencia a Fracturas1
Flexibilidad sin precedentes,33 que imita la estructura natural y el movimiento de la anatomía35-37
Cero fracturas de stent reportadas a 1 año en más de 2,000 pacientes en 17 estudios1,15-30

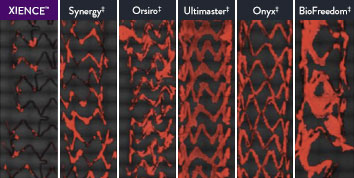
The XIENCE™ Stent is also recognized as being significantly more anti-thrombotic than other DES on the market. As shown in the study findings, XIENCE™ Stent reveals significantly less (p < 0.01) platelet adhesion—shown in red in the confocal microscopy images—than other DES, and platelet adhesion is an important factor in stent thrombosis.*8 These findings suggest that this stent choice “may be ideally suited for very short-term DAPT.”8
*Ex Vivo Swine Shunt Model.

Diamondback 360™ OAS Gives You the Versatility to Treat Challenging Cases
Treat even the most severely calcified lesions, with under 2-minute setup7,8 and predictable procedure times.2
Facilitates antegrade and retrograde treatment of:
- Long, Diffuse Lesions
Successfully treated lesions up to 60 mm in length in real-world study.9 - Heavily Stenosed Lesions
Crossed >99% of lesions with <2% pre-dilatation in the ORBIT II study.1,10 - Nodular Lesions
Effectively treats nodular calcification.5,6 - Ostial Lesions
Safely treats ostial lesions.11-13
Low Profile
6F compatible for femoral or radial access.14
Multiple Vessel Sizes
A single 1.25 mm crown treats vessels 2.5 mm to 4.0mm14
|
|
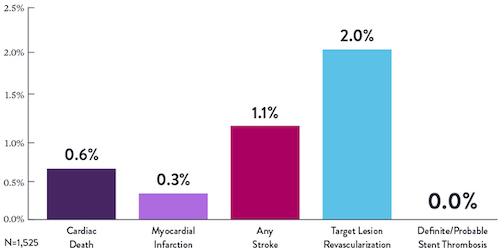
Proven Safety |
Procedural Success |
Low Q-Wave MI Rate |
>2,200 |
<1% |
97.7% |
0.9% |
|
Patients Across 11 |
Component Angiographic |
Crossing and Stent |
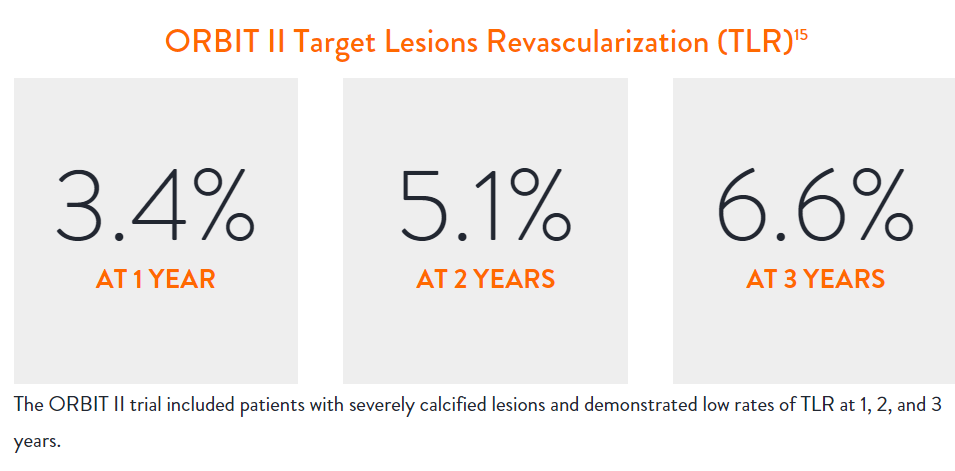
In the ORBIT II |
Sustained Clinical Performance
Data are for ORBIT II TLR in the OA+DES patient cohort.

“Stopping DAPT at 3 months in selected patients after [XIENCE™ Stent] implantation was at least as safe as the prolonged DAPT regimen adopted in the historical control group.”
— Masahiro Natsuaki, MD, STOPDAPT Trial9

STOPDAPT 2 Trial Design and Randomization10

Short 1-Month DAPT
- 0 to 1-month: Aspirin + P2Y12
- After 1-month: Clopidogrel monotherapy

12-Month DAPT
- 0 to 1-month: Aspirin + P2Y12
- 1 to 12-month: Aspirin + Clopidogrel
- 12 to 60-month: Aspirin monotherapy

- Successful PCI using CoCr everolimus-eluting stent: XIENCE™
- Eligible for DAPT (aspirin/P2Y12 receptor blocker) for 1 year

- Patients who need oral anticoagulants
- History of intracranial bleeding
- Major in-hospital complications (MI/stroke/major bleeding)
STOPDAPT Study: XIENCE™ Stent with 3-Month DAPT Is Feasible9
STOPDAPT9 was the first prospective trial to study DAPT cessation at 3 months after implantation. Among other 1-year outcomes, the XIENCE™ Stent rate of stent thrombosis was 0.0%.
STOPDAPT Study Demonstrates Feasibility of XIENCE™ Stent with 3-Month DAPT9

Learn more about STOPDAPT 2

“It was noteworthy that no definite or probable stent thrombosis occurred in [XIENCE™ Stent] patients enrolled in STOPDAPT.”
— Masahiro Natsuaki, MD, STOPDAPT Trial9

STOPDAPT-3 Trial Design and Randomization11

- PCI with planned exclusive use of CoCr-EES (XIENCE)
- ACS presentation or ARC-HBR
- Eligible for DAPT (Aspirin/P2Y12inhibitor) for 1 month
Study design and Randomization
Group 1:
0 to 1-month: Aspirin + P2Y12 (Prasugrel)
After 1-month: Clopidogrel monotherapy
Group 2:
0 to 1-month: P2Y12 (Prasugrel)
After 1-month: Clopidogrel monotherapy
STOPDAPT-3 Trial 11 was designed to explore 0-month DAPT* (SAPT˄ using only P2Y12 inhibitor) for ACS and HBR patients.
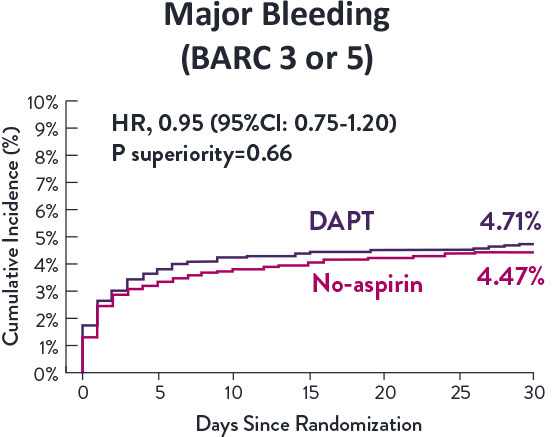
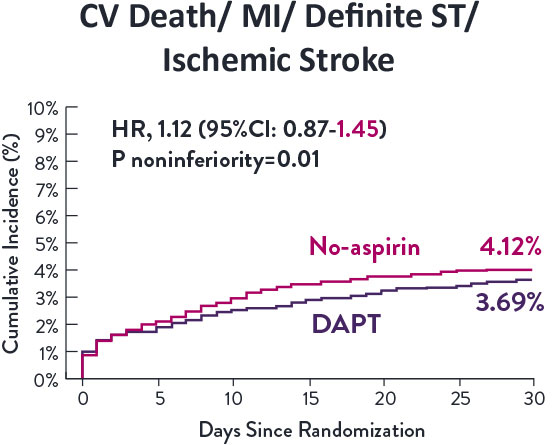
Though the results are comparable for both bleeding and ischemic events for DAPT and SAPT arms, the study did not meet its endpoint and concluded to use DAPT for 1 month after PCI.
XIENCE™ Stent remains the ONLY DES with the shortest DAPT indication, as short as 28 days.12


Referencias
- Garcia L. et al., Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2017 Jun 1;89(7):1259-1267.
- Dake M. et al., Circulation. 2016;133:1472-1483.
- Laird J. et al., Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3:267-276.
- Laird J et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2012;19:1–9.
- S.M.A.R.T. Control IFU.
- Jaff, M., SMART Nitinol Self-Expanding Stent in the Treatment of Obstructive Superficial Femoral Artery Disease: Three-year Clinical Outcomes from the STROLL Trial. ISET 2014.
- Matsumura J et al., J Vasc Surg 2013;58:73-83.
- Rocha-Singh, K., 3-Year Results of the DURABILITY II Study. VIVA 2013.
- US Innova IFU.
- US Pulsar IFU.
- Ohki T. et al. J Vasc Surg. 2016 Feb;63(2):370-6.
- Gray W. et al., Lancet 2018;392:1541-51.
- Treitl, K.M., et al. European Radiology. 2017; 10.1007.
- Palena L.M. et al. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Intervention. 2016.
- Brescia AA. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2015 Jun;61(6):1472-8
- George JC. et al., J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014 Jun;25(6):954-61.
- Montero-Baker M. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2016 Oct;64(4):1002-8.
- Scheinert D. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2011 Dec;18(6):745-52.
- Werner M. et al., EuroIntervention. 2014 Nov;10(7):861-8.
- San Norberto EM. et al., Ann Vasc Surg. 2017 May;41:186-195.
- Chan YC. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2015 Nov;62(5):1201-9.
- Dumantepe M. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2017 Jul;51(5):240-246.
- Goltz JP. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2012 Jun;19(3):450-6.
- León LR Jr. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2013 Apr;57(4):1014-22.
- Myint M. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2016 Jun;23(3):433-41.
- Palena LM. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2018 Oct;25(5):588-591.
- Scheinert D. et al., JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Jan;6(1):65-71.
- Steiner S. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2016 Apr;23(2):347-55.
- Teymen B. et al., Vascular. 2018 Feb;26(1):54-61.
- Bhatt H. et al., Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2018 Jul;19(5 Pt A):512-515.
- Garcia L. et al. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:e000937
- Competitors tested include Astron Pulsar-18, Complete SE, EverFlex, Innova, LifeStent, Misago, S.M.A.R.T., and Zilver PTX. Data on file at Abbott.
- Flexibility is defined as kink resistance. Competitors tested include Astron Pulsar-18, Complete SE, EverFlex, Innova, LifeStent, Misago, S.M.A.R.T., and Zilver PTX. Data on file at Abbott.
- Zhao HQ et al. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009;32(4):720-6
- Arena F. et al., J Vasc Med Surg. 2013:1;116.
- Chen Y. et al., J Vasc Surg 2014;59:384-91.
- Data on file at Abbott.

MAT-XXXXXXX



