

The Scaffold is Gone, But the Benefit Remains
| LIFE-BTK Study Results | LIFE-BTK Study Design |
Clinical Follow-Up
LIFE-BTK Study Results
Superior Efficacy at 1 Year2, Sustained Benefits through 3 Years1
| Esprit™ BTK offers continued long-term benefits vs PTA, particularly in terms of limb salvage and primary patency through 3 years. A clear advantage over PTA in terms of sustained vascular patency and limb preservation.1 | 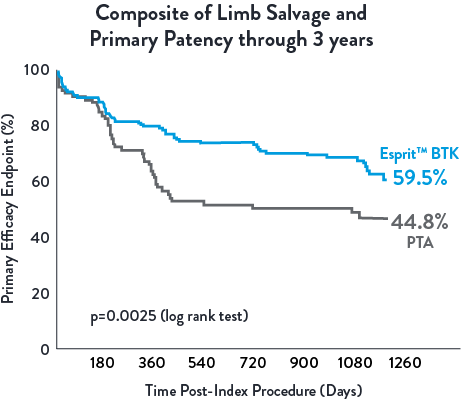 |
Low Reintervention Rate in CLTI Patients through 3 years1
| Esprit™ BTK reduces binary restenosis and total occlusion, due to its biological efficacy and resorbable mechanical support. Esprit™ BTK demonstrates long-term durability, effectively reducing restenosis and promoting long-term vessel patency.1,2 | 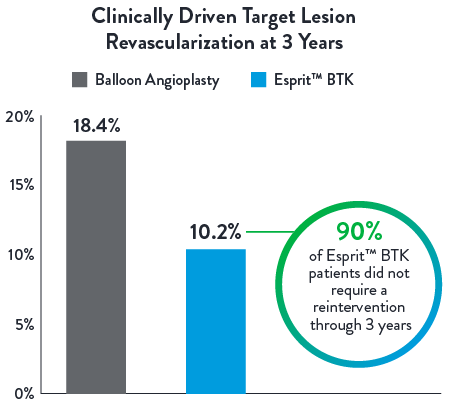 |
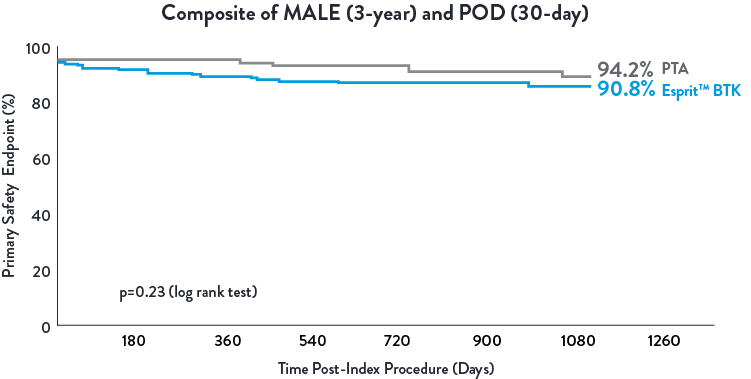
Esprit™ BTK demonstrated to be as safe as balloon angioplasty, maintained at 3 years.1
LIFE-BTK Study Design*
The LIFE-BTK Study is a prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the Esprit™ BTK Everolimus Eluting Resorbable Scaffold System vs percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA)† for the treatment of infrapopliteal arterial disease in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI).
- Prospective, randomized, multicenter trial across 50 Global Sites
- 261 patients randomized (2:1 Esprit™ BTK System vs. PTA†)
- Esprit™ BTK System (n=173)
- PTA† (n=88)
** Follow up focused on index wound assessment
† defined as Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty
Sites and Enrollment
Total Enrolled Sites: 50 | Total Randomized Patients: 261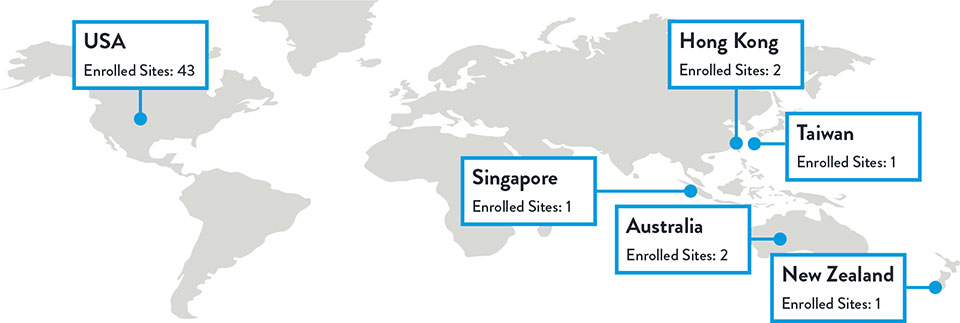
Varcoe, R. Primary Outcomes of the Esprit™ BTK Drug-Eluting Resorbable Scaffold for the Treatment of Infrapopliteal Lesions: The LIFE-BTK Trial. Presented at TCT 2023
Race, Gender, and Ethnicity Distribution
Multiple studies have shown racial and ethnic disparities in the prevalence of PAD and CLTI, as well as in access to and outcomes of treatment4,5
The LIFE-BTK trial was designed and conducted to include a diverse patient population representative of those most affected by the disease6
Race, Gender, and Ethnicity Distribution
Gender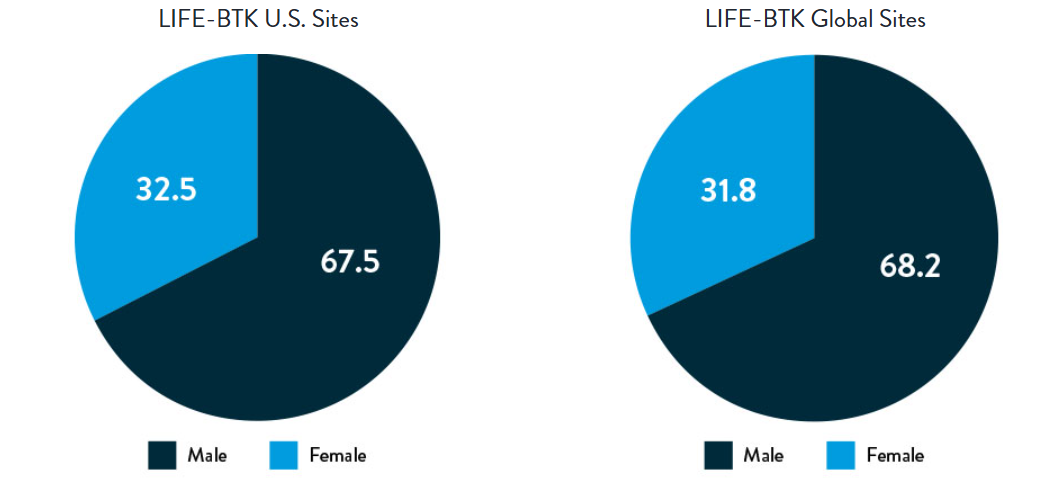
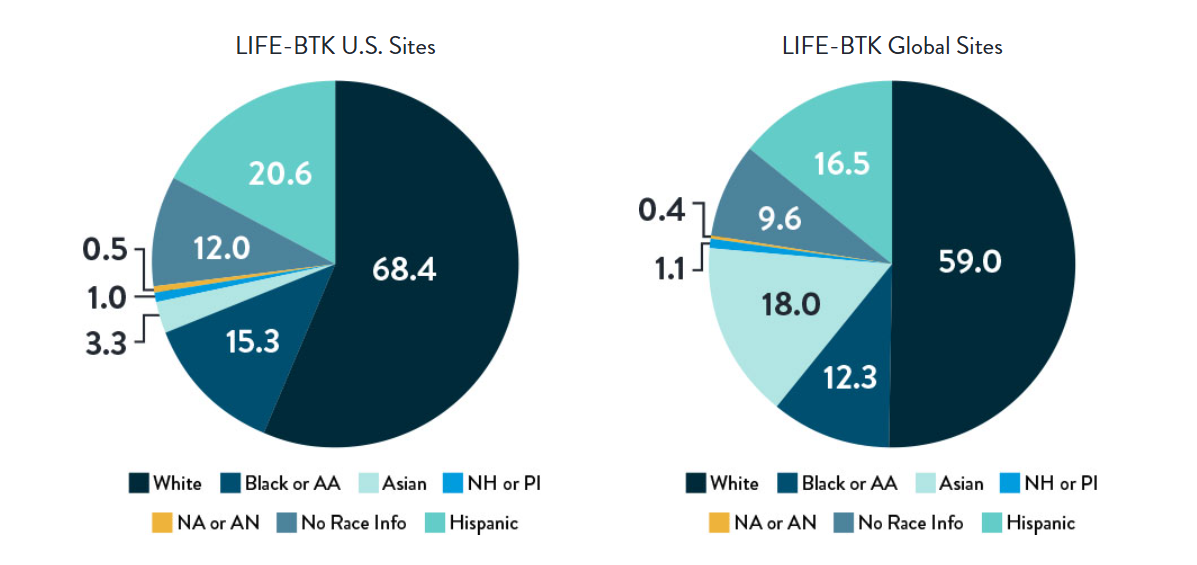
Race and Ethnicity
AA: African American | NH: Native Hawaiian | PI: Pacific Islander | NA: North American Native/American Indian | AN: Alaska Native
Varcoe, R. Primary Outcomes of the Esprit™ BTK Drug-Eluting Resorbable Scaffold for the Treatment of Infrapopliteal Lesions: The LIFE-BTK Trial. Presented at TCT 2023
Proven Efficacy and Durability Across Diverse Races and Ethnicities
Composite Primary Effectiveness Endpoint at 1 Year
The primary and secondary endpoint results for different race and ethnicity subgroups were consistent with the overall population, demonstrating the Esprit™ BTK device’s biological efficacy, durability, and robust performance across diverse patient populations5.
Race and Ethnicity Subgroup Analysis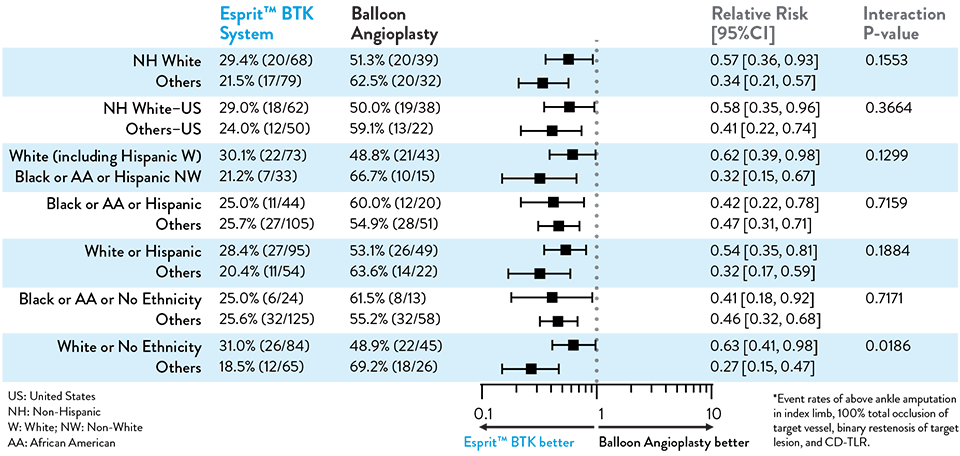
LIFE-BTK 1Y Endpoints2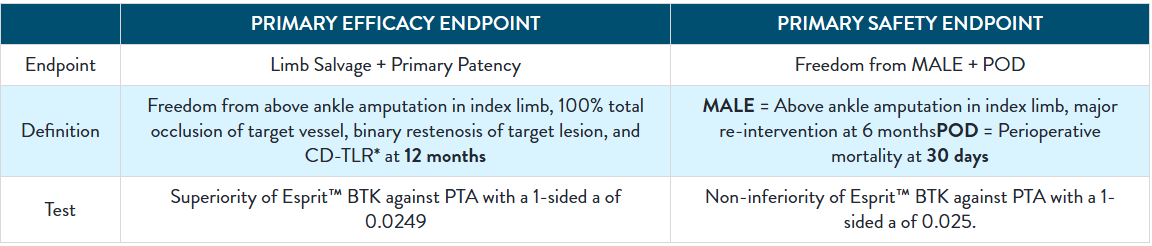
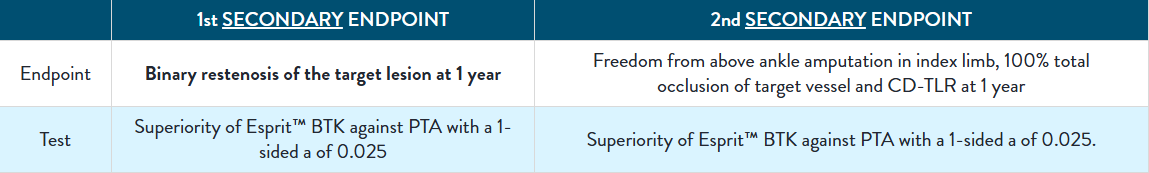
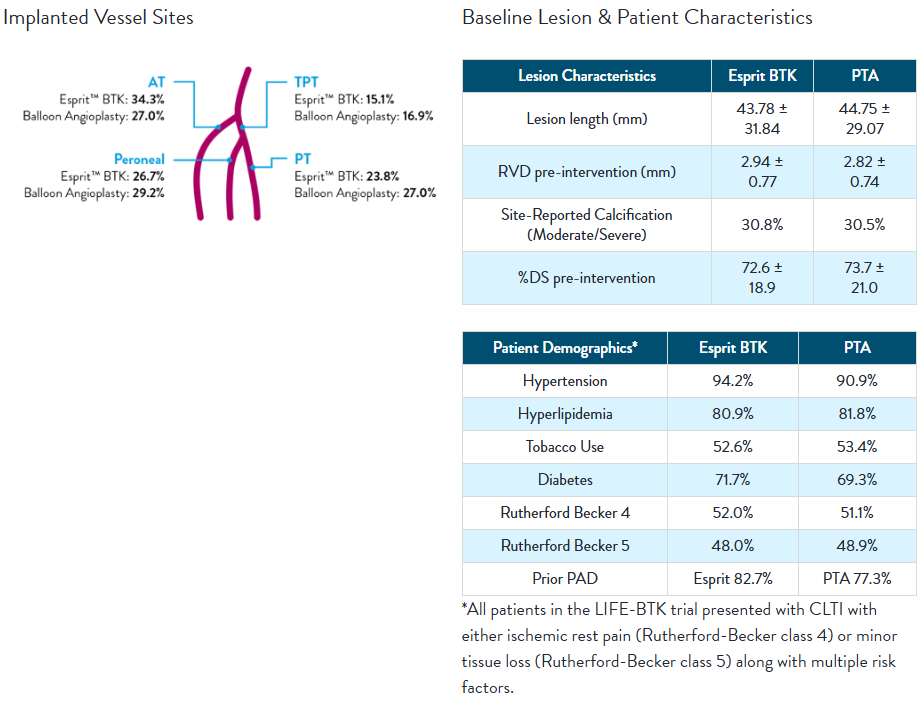
Consistently Higher Observed Rate of Limb Salvage and Primary Patency With Esprit™ BTK Across a Range of Lesion Lengths Up to 148 mm
Primary Efficacy Endpoint
Composite of Limb Salvage and Primary Patency at 1 Year
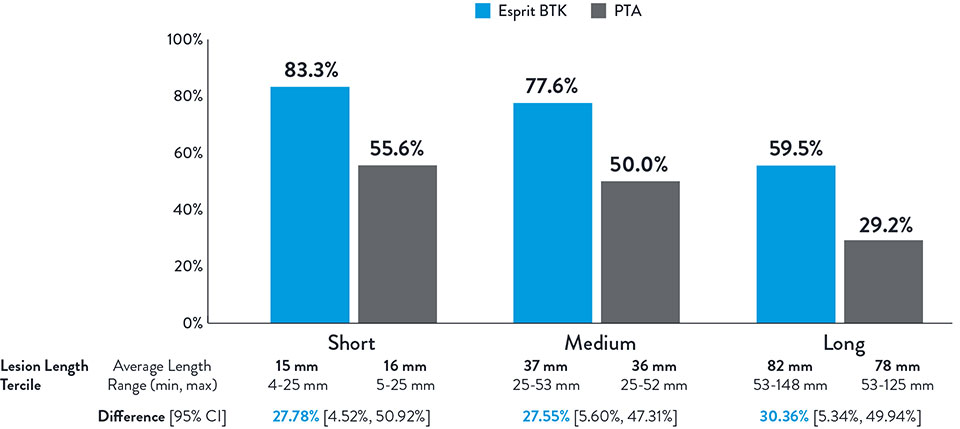
NOTE: Post-hoc subgroup analysis by lesion length terciles was conducted where no pre-specified hypothesis testing was completed to provide a p-value.
Varcoe, Ramon L., et. al. "Supplementary Appendix." In "Drug-eluting resorbable scaffold versus angioplasty for infrapopliteal artery disease." New England Journal of Medicine. 390 (2024): 9-19.

Resultados del Estudio XIENCE 28 y XIENCE 906
Stent XIENCE™ con DAPT a corto plazo: Eventos isquémicos
Entre los pacientes con alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR), el stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 1 o 3 meses redujo el sangrado grave sin aumento en los eventos isquémicos, incluido el infarto de miocardio (IM) y todas las muertes.6
XIENCE 28: DAPT de 1 mes en pacientes con alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR)
XIENCE 28: Todas las muertes o IM
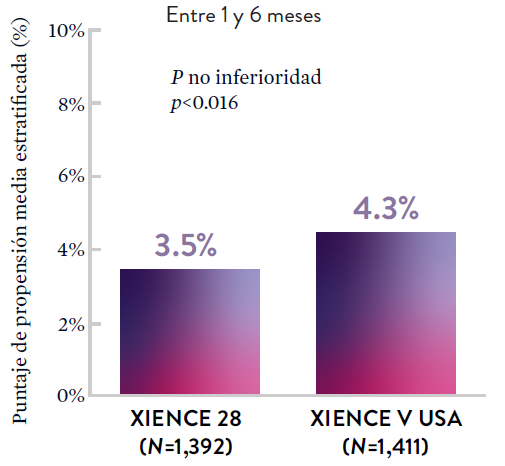
XIENCE 90: DAPT de 1 mes en Pacientes con alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR)
XIENCE 90: Todas las muertes o IM
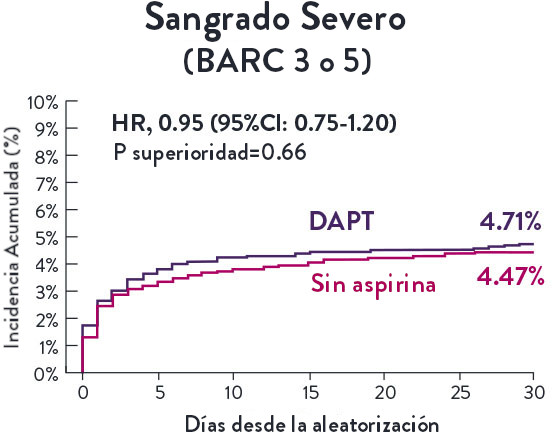
Stent XIENCE™ con DAPT a corto plazo: Reducción del sangrado severo
En la misma población de pacientes con alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR), el stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 1 o 3 meses redujo el sangrado severo sin aumento en los eventos isquémicos.6,*
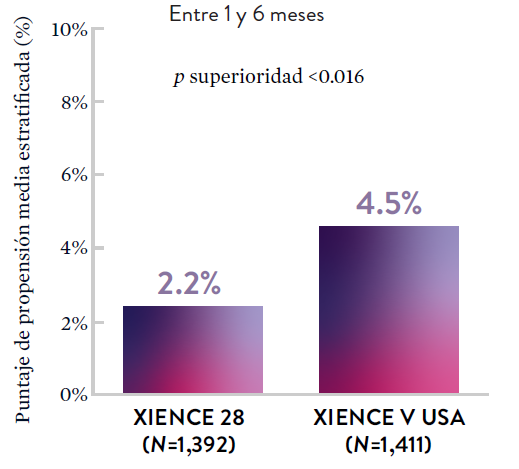
XIENCE 28: Sangrado BARC 3-5
XIENCE 90: Sangrado BARC 3-5
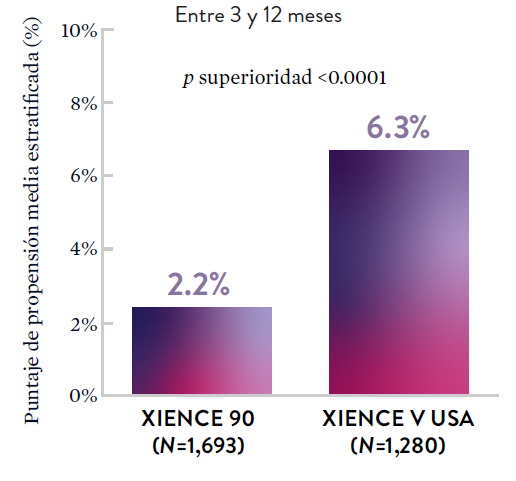
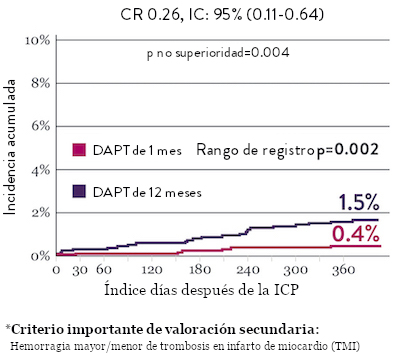
*El análisis estratificado por puntaje de propensión para el sangrado BARC 3-5 no fue preespecificado. BARC 2-5 fue un criterio de evaluación secundario reforzado para su significación estadística. En ambos estudios, para BARC 2-5, el stent XIENCE™ mostró una tasa de sangrado numéricamente menor para DAPT de 1 o 3 meses frente a una DAPT de 6 meses o DAPT de 12 meses, respectivamente.
Stent XIENCE™ con DAPT a corto plazo: Baja tasa continua de trombosis del stent
El stent XIENCE™ es reconocido por sus tasas bajas de trombosis del stent (ST), y es significativamente más tromborresistente que otros DES.7 Esto es evidente, incluso con datos de DAPT a corto plazo. El stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 1 mes no mostró aumento en la ST frente a una DAPT de 6 meses, con una tasa de ST de 0.3%. De manera similar, el DAPT de 3 meses mostró una tasa de ST de 0.2%.6
XIENCE 28: Trombosis del stent (ST)
Entre 1 y 6 meses
ARC: ST Definitiva/Probable
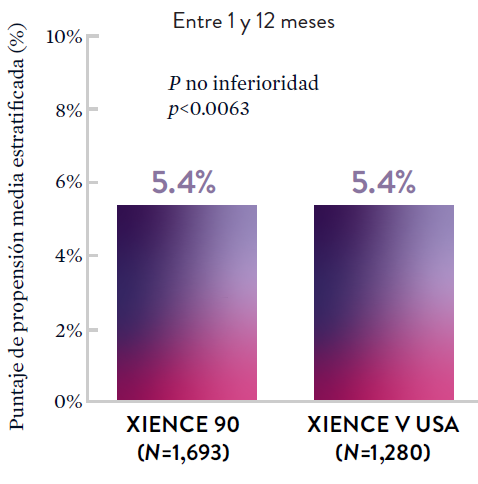
El stent XIENCE™ con DAPT corto muestra tasas consistentemente bajas de trombosis del stent: DAPT de 1 y 6 meses son ambos de 0,3% ST, y DAPT de 3 y 12 meses son ambos de 0,2% ST.XIENCE 90: Trombosis del stent (ST)
Entre 3 y 12 meses
ARC: ST Definitiva/Probable
El stent XIENCE™ con DAPT corto muestra tasas consistentemente bajas de trombosis del stent: DAPT de 1 y 6 meses son ambos de 0,3% ST, y DAPT de 3 y 12 meses son ambos de 0,2% ST.El stent XIENCE™ es tromborresistente: Adecuado para la DAPT a corto plazo
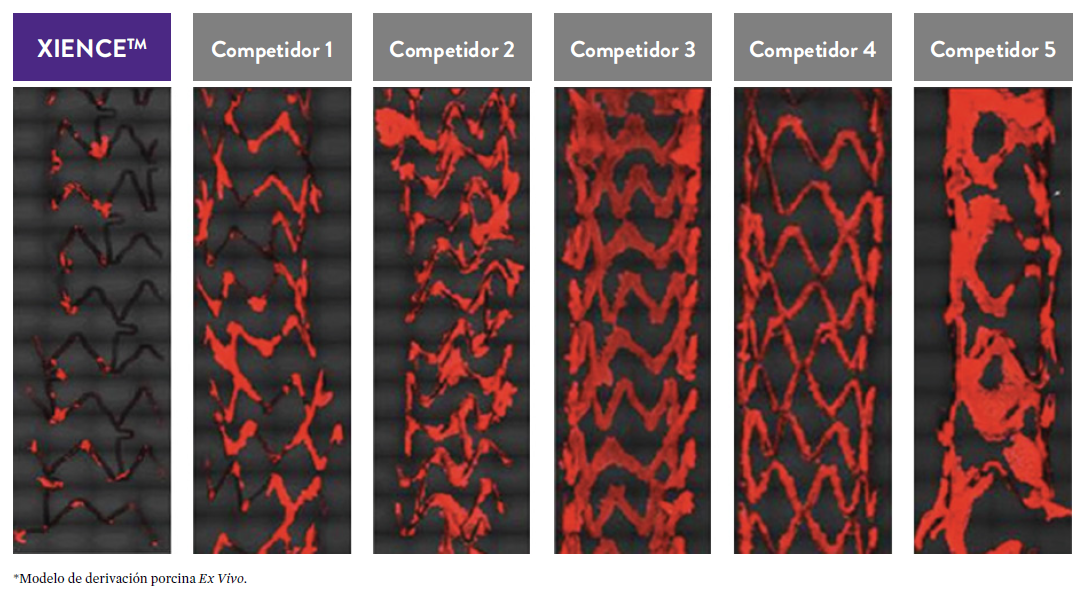
El stent XIENCE™ también es reconocido por ser significativamente más tromborresistente que otros DES disponibles en el mercado. Como muestran los hallazgos del estudio, el stent XIENCE™ muestra significativamente menor adhesión plaquetaria (p<0.01) en comparación con otros DES — como se muestra en rojo en las imágenes de microscopía confocal. La adhesión plaquetaria es un factor importante en la trombosis del stent.*8 Estos hallazgos sugieren que esta elección de stent "puede ser idealmente adecuada para DAPT a muy corto plazo".8
*Modelo de desviación ex-vivo en cerdos.

Estudios STOPDAPT: DAPT de 1 mes y 3 meses en una población general9,10
STOPDAPT9 y STOPDAPT 210 fueron ensayos prospectivos del stent XIENCE™ que estudiaron la interrupción de la DAPT a los 3 meses y 1 mes, respectivamente.
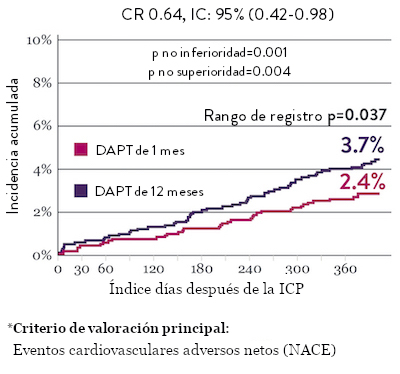
Ensayo STOPDAPT 2: DAPT de 1 mes superior a la DAPT de 12 meses10
El ensayo STOPDAPT 2 reveló que la DAPT de 1 mes demostró seguridad superior a la DAPT de 12 meses, para el criterio de valoración principal de eventos cardiovasculares adversos netos (NACE, por sus siglas en inglés). El NACE incluyó muerte cardiovascular, infarto de miocardio (IM), trombosis del stent (ST) definitiva, accidente cerebrovascular o hemorragia mayor/menor de trombosis en infarto al miocardio (TIMI, por sus siglas en inglés). Los 3,009 pacientes de este ensayo controlado y aleatorizado fueron tratados con el stent XIENCE™.10
NACE* significativamente menor con DAPT de 1 mes
Sangrado significativamente menor* con DAPT de 1 Mes
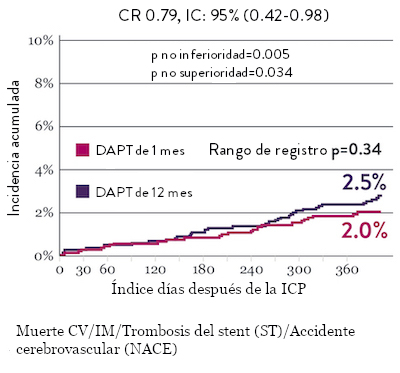
Tasas de eventos isquémicos comparables* con DAPT de 1 mes

“Interrumpir la DAPT a los 3 meses en pacientes seleccionados después de la implantación [del stent XIENCE™] fue tan seguro como el régimen prolongado de DAPT adoptado en el grupo de control histórico.”
— Masahiro Natsuaki, MD, Ensayo STOPDAPT9

Diseño y aleatorización del Ensayo STOPDAPT 210

DAPT corto de 1 mes
- 0 a 1-mes: Aspirina + P2Y12
- Después de 1 mes: Monoterapia con clopidogrel

DAPT de 12 meses
- 0 a 1 mes: Aspirina + P2Y12
- 1 a 12 meses: Aspirina + Clopidogrel
- 12 a 60 meses: Monoterapia con aspirina

- Intervención coronaria percutánea (ICP) exitosa utilizando un stent liberador de everolimus de cobalto-cromo: XIENCE™
- Candidato para DAPT (aspirina/inhibidor del receptor P2Y12) durante 1 año

- Pacientes que necesitan anticoagulantes orales
- Historial de hemorragia intracraneal
- Complicaciones importantes en el hospital (IM/accidente cerebrovascular/hemorragia mayor)
Ensayo STOPDAPT: La combinación del stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 3 meses es factible9
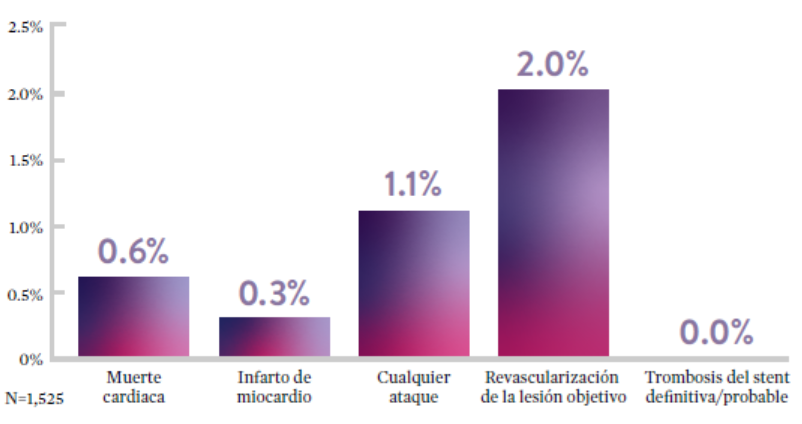
STOPDAPT9 fue el primer ensayo prospectivo que estudió la interrupción de la DAPT a los 3 meses después de la implantación. Entre otros resultados a 1 año, la tasa de trombosis de stent con XIENCE™ fue de 0.0%.
El ensayo STOPDAPT demuestra la factibilidad de usar el stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 3 meses9

Conozca más acerca de STOPDAPT 2

“Vale la pena destacar que no se produjo ninguna trombosis de stent definitiva o probable en los pacientes tratados con XIENCE™ incluidos en STOPDAPT.”
— Masahiro Natsuaki, MD, Ensayo STOPDAPT9

STOPDAPT-3 Trial Design and Randomization11

- ICP con uso exclusivo y planificado de un stent liberador de everolimus (EES, por sus siglas en inglés ) de CoCr (XIENCE™)
- Presencia de paro cardíaco súbito (SCA, por sus siglas en inglés) o ARC-HBR
- Elegible para DAPT (aspirina/inhibidor P2Y12) durante 1 mes.
Diseño del estudio y aleatorización
Grupo 1:
0 a 1 mes: Aspirina + P2Y12 (Prasugrel)
Después de 1 mes: Monoterapia con clopidogrel
Grupo 2:
0 a 1 mes: P2Y12 (Prasugrel)
Después de 1 mes: Monoterapia con clopidogrel
El Ensayo STOPDAPT-311 se diseñó para estudiar la DAPT de 0 meses* (SAPT˄ utilizando solamente un inhibidor P2Y12) para pacientes con paro cardiaco súbito (SCA) y alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR).
Aunque los resultados son comparables tanto para hemorragias como para eventos isquémicos en los brazos de DAPT y TAPS, el estudio no cumplió con su criterio de valoración y concluyó en usar DAPT durante 1 mes después de la ICP.

El stent XIENCE™ sigue siendo el ÚNICO DES con la indicación de DAPT más corta, que puede ser tan corta como 28 días.12


References:
*Re-intervention defined as CD-TLR.
- Parikh, S., Three-Year Outcomes of the LIFE-BTK Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating the Esprit™ BTK Drug-Eluting Resorbable Scaffold for Treatment of Infrapopliteal Lesions, Presented at TCT 2025.
- Varcoe, RL., et al. Drug-Eluting Resorbable Scaffold versus Angioplasty for Infrapopliteal Artery Disease. N Eng J Med 2024;390:9-19.
- Brian G. DeRubertis et al., Drug-Eluting Resorbable Scaffold Versus Balloon Angioplasty for Below-the-Knee Peripheral Artery Disease: 2-Year Results From the LIFE-BTK . Circulation 2025.
- Eid MA, et al. Semin Vasc Surg. 2021;34(1):38-46.
- Chen L, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:692236.
- Garcia, LA, et al. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in the LIFE-BTK Trial Evaluating the Esprit™ BTK Drug-Eluting Resorbable Scaffold for the Treatment of Infrapopliteal Lesions in Patients with Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia, VIVA 2024.

MAT-XXXXXXX



