


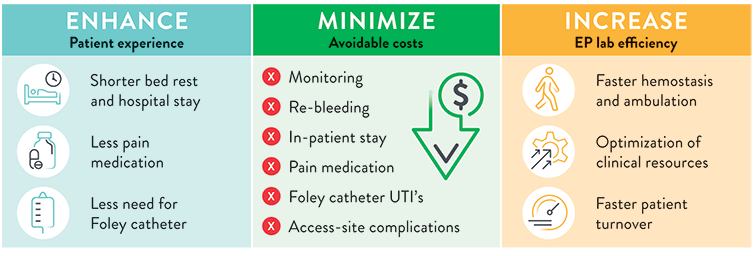
Whether you use RF, Cryo, or Pulse Field Ablations, the comprehensive Perclose™ Systems allow you to confidently adopt innovations with larger sheath sizes.1, §
Learn more about how you can finish your procedure with confidence

The Perclose™ ProStyle™ closure device achieves rapid hemostasis of femoral access sites by approximating the edges of the vessel wall with a surgical suture. The benefits of suture-mediated repair include promoting primary intention healing with less scarring18 and decreased time to hemostasis, ambulation, and patient discharge.4,19
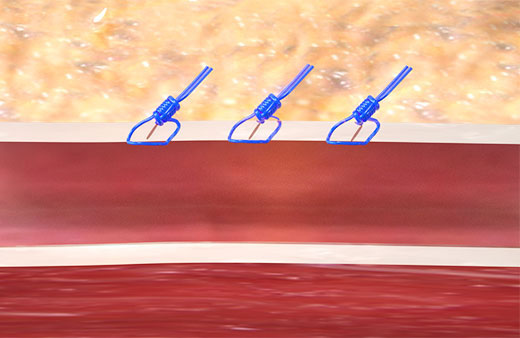
Unlike collagen based VCDs,† Perclose™ Prostyle™ has no re-access restrictions.1

Before and After Choosing the Perclose™ ProStyle™ Device
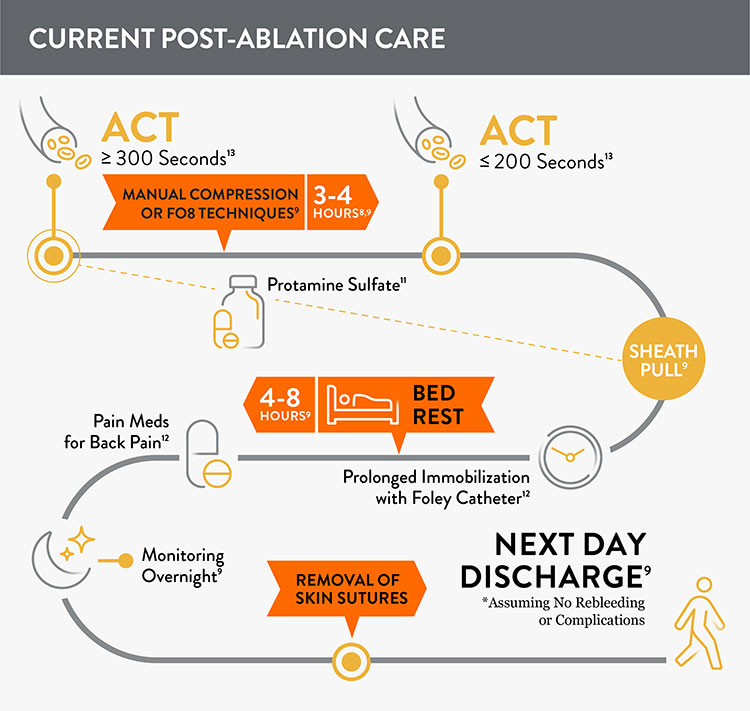
Prior to adopting Perclose™ ProStyle™ SMCR System, EPs completing an atrial fibrillation ablation or other procedures may find that patients require:
- Multiple venous sheaths and access sites8
- Uninterrupted anticoagulation: activated clotting time (ACT) ≥ 300 seconds9,10
- Manual compression at groin access site for up to 30 minutes9
- Protamine sulfate to reverse the effects of heparin11
- Figure-of-eight (FO8) to maintain hemostasis9
- Prolonged immobilization/bedrest of 4-12 hours to prevent bleeding and complications9
- A Foley catheter12
- Discharge 249-7210 hours after the procedure
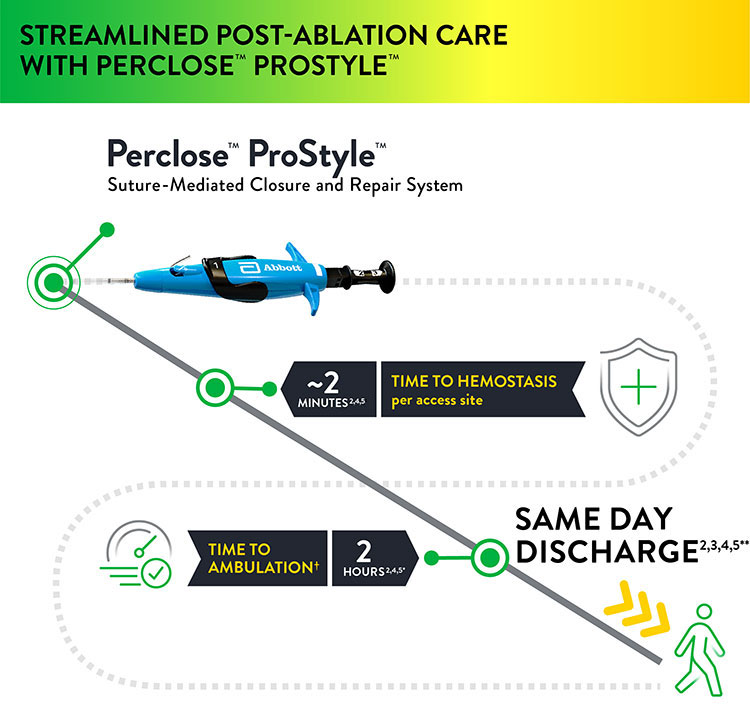
The Perclose™ ProStyle™ closure device transforms an otherwise lengthy patient recovery to a shorter recovery time, which in turn leads to a positive patient experience:
- Time to hemostasis (TTH) on avg is ~2 minutes per access site2,4,5
- Patient may sit up immediately; no lay-flat restrictions1
- Patients can ambulate after 2 hours1
- Patient may be eligible for same-day discharge2,3,4,5**

The use of Perclose™ ProStyle™ Suture-Mediated Closure and Repair System can help:

Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, Perclose™ ProStyle™ can be used in conjunction with a variety of AFib ablation techniques, including Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA) for venous sheaths up to 24F ID (29 OD).1†
At the time of this publication, only Perclose™ Devices can close after all PFA systems including Farapulse‡ (13F Inner Diameter (ID), 16.8F Outer Diameter (OD)). §,1,†
Using a VCD has several advantages given the following factors during EP procedures such as AF ablations:
- Physicians often have multiple access sites to manage, even some involving large caliber venous sheaths.8
- Patients often receive full-dose peri-procedural anticoagulation, and this can make complete hemostasis a challenging and lengthy process, requiring prolonged immobilization.9,10
- The typical EP lab post-procedure process requires the patient to remain immobilized for prolonged periods of time, which is a source of patient discomfort.9
Yes, Same-Day Discharge has been shown to be safe, and it is being used to reduce the total cost of care and to enhance the patient experience. The use of vessel closure devices makes it possible for hospitals to implement Same-Day Discharge.4,17,20,21
With the Perclose™ ProStyle™ device you can achieve and confirm complete hemostasis on the table with a suture-mediated repair of the access site. Other advantages of the Perclose ProGlide™ SMC System include:
- The broadest indication† for use in both common femoral veins and arteries
- No ACT-level requirements, so reversal of heparin is not required in order to achieve immediate and durable hemostasis1,13
For what range of sheath sizes and devices can the Perclose™ ProStyle™ SMCR System be used?
The Perclose ProStyle™ closure device is indicated for use with:
- Venous sheaths 5-24F1 (Max. OD 29F22 / 0.378 inches / 9.59 mm)
- Arterial sheaths 5-21F1 (Max OD 26F22 / 0.340 inches / 8.62 mm)
No, there is only one Perclose™ ProStyle™ SMCR System. Multiple Perclose™ ProStyle™ devices can be used, if necessary, for large-bore vascular closure.
How quickly can a patient be mobilized, ambulated, and discharged when using the Perclose™ ProStyle™ closure device?
Because this device achieves immediate and durable hemostasis, patients may sit up immediately in bed.1 Clinical evidence for cardiac arrhythmia treatments with multiple access sites has shown that patients safely ambulated within 2 hours2,4,5,* and were eligible for same-day discharge after successfully closing with Perclose™ devices.2,3,4,5**
How does the Perclose™ ProStyle™ SMCR System achieve immediate and durable hemostasis?
It achieves hemostasis by approximating the edges of the vessel wall with a surgical suture, allowing primary intention healing to begin. Primary intention healing minimizes scarring and allows for immediate reaccess if needed. View primary intention healing images with vessel closure device.18
What kind of training is available to begin using the Perclose™ ProStyle™ SMCR System?
Contact your local Abbott representative for a training opportunity.
What is the "Pre-Close" Technique?
The "Pre-Close" Technique involves the Perclose™ ProStyle™ suture being placed around the access site before the index procedure, and it is required before using sheath sizes > 8F.1
See Deployment and Instructions for Use for additional information.

Resultados del Estudio XIENCE 28 y XIENCE 906
Stent XIENCE™ con DAPT a corto plazo: Eventos isquémicos
Entre los pacientes con alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR), el stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 1 o 3 meses redujo el sangrado grave sin aumento en los eventos isquémicos, incluido el infarto de miocardio (IM) y todas las muertes.6
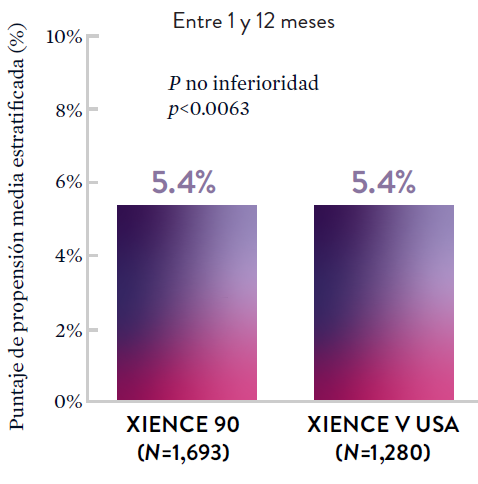
XIENCE 28: DAPT de 1 mes en pacientes con alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR)
XIENCE 28: Todas las muertes o IM
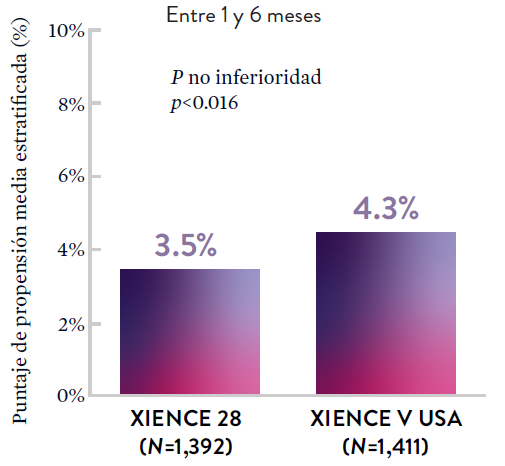
XIENCE 90: DAPT de 1 mes en Pacientes con alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR)
XIENCE 90: Todas las muertes o IM
Stent XIENCE™ con DAPT a corto plazo: Reducción del sangrado severo
En la misma población de pacientes con alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR), el stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 1 o 3 meses redujo el sangrado severo sin aumento en los eventos isquémicos.6,*
XIENCE 28: Sangrado BARC 3-5
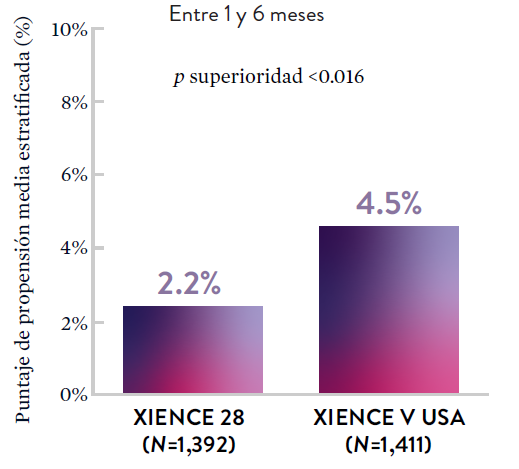
XIENCE 90: Sangrado BARC 3-5
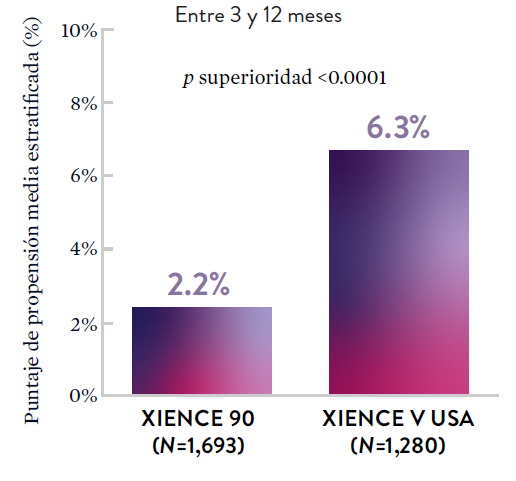
*El análisis estratificado por puntaje de propensión para el sangrado BARC 3-5 no fue preespecificado. BARC 2-5 fue un criterio de evaluación secundario reforzado para su significación estadística. En ambos estudios, para BARC 2-5, el stent XIENCE™ mostró una tasa de sangrado numéricamente menor para DAPT de 1 o 3 meses frente a una DAPT de 6 meses o DAPT de 12 meses, respectivamente.
Stent XIENCE™ con DAPT a corto plazo: Baja tasa continua de trombosis del stent
El stent XIENCE™ es reconocido por sus tasas bajas de trombosis del stent (ST), y es significativamente más tromborresistente que otros DES.7 Esto es evidente, incluso con datos de DAPT a corto plazo. El stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 1 mes no mostró aumento en la ST frente a una DAPT de 6 meses, con una tasa de ST de 0.3%. De manera similar, el DAPT de 3 meses mostró una tasa de ST de 0.2%.6
XIENCE 28: Trombosis del stent (ST)
Entre 1 y 6 meses
ARC: ST Definitiva/Probable
El stent XIENCE™ con DAPT corto muestra tasas consistentemente bajas de trombosis del stent: DAPT de 1 y 6 meses son ambos de 0,3% ST, y DAPT de 3 y 12 meses son ambos de 0,2% ST.XIENCE 90: Trombosis del stent (ST)
Entre 3 y 12 meses
ARC: ST Definitiva/Probable
El stent XIENCE™ con DAPT corto muestra tasas consistentemente bajas de trombosis del stent: DAPT de 1 y 6 meses son ambos de 0,3% ST, y DAPT de 3 y 12 meses son ambos de 0,2% ST.El stent XIENCE™ es tromborresistente: Adecuado para la DAPT a corto plazo
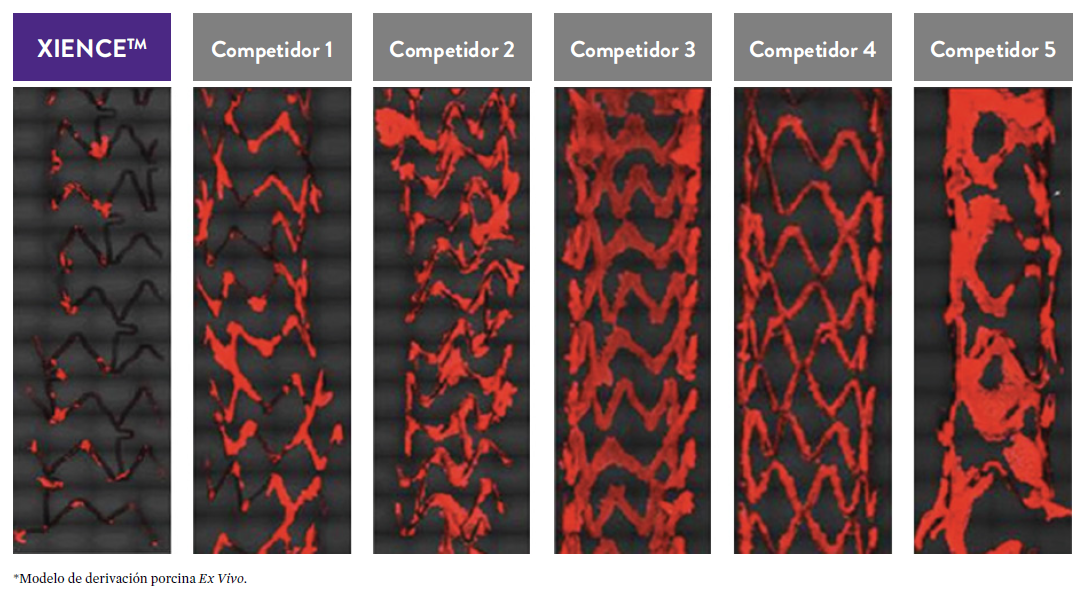
El stent XIENCE™ también es reconocido por ser significativamente más tromborresistente que otros DES disponibles en el mercado. Como muestran los hallazgos del estudio, el stent XIENCE™ muestra significativamente menor adhesión plaquetaria (p<0.01) en comparación con otros DES — como se muestra en rojo en las imágenes de microscopía confocal. La adhesión plaquetaria es un factor importante en la trombosis del stent.*8 Estos hallazgos sugieren que esta elección de stent "puede ser idealmente adecuada para DAPT a muy corto plazo".8
*Modelo de desviación ex-vivo en cerdos.

Estudios STOPDAPT: DAPT de 1 mes y 3 meses en una población general9,10
STOPDAPT9 y STOPDAPT 210 fueron ensayos prospectivos del stent XIENCE™ que estudiaron la interrupción de la DAPT a los 3 meses y 1 mes, respectivamente.
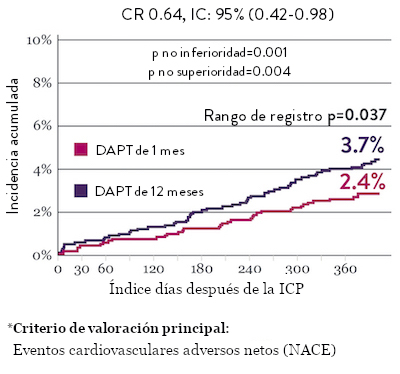
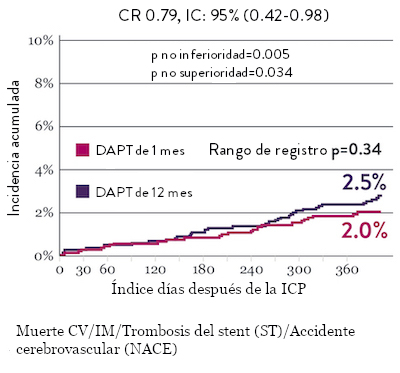
Ensayo STOPDAPT 2: DAPT de 1 mes superior a la DAPT de 12 meses10
El ensayo STOPDAPT 2 reveló que la DAPT de 1 mes demostró seguridad superior a la DAPT de 12 meses, para el criterio de valoración principal de eventos cardiovasculares adversos netos (NACE, por sus siglas en inglés). El NACE incluyó muerte cardiovascular, infarto de miocardio (IM), trombosis del stent (ST) definitiva, accidente cerebrovascular o hemorragia mayor/menor de trombosis en infarto al miocardio (TIMI, por sus siglas en inglés). Los 3,009 pacientes de este ensayo controlado y aleatorizado fueron tratados con el stent XIENCE™.10
NACE* significativamente menor con DAPT de 1 mes
Sangrado significativamente menor* con DAPT de 1 Mes
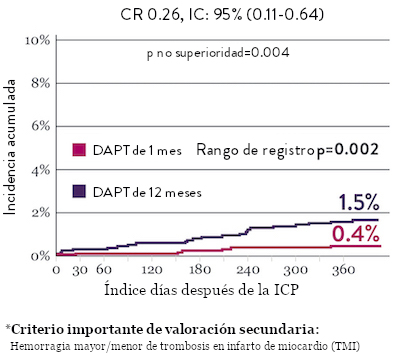
Tasas de eventos isquémicos comparables* con DAPT de 1 mes

“Interrumpir la DAPT a los 3 meses en pacientes seleccionados después de la implantación [del stent XIENCE™] fue tan seguro como el régimen prolongado de DAPT adoptado en el grupo de control histórico.”
— Masahiro Natsuaki, MD, Ensayo STOPDAPT9

Diseño y aleatorización del Ensayo STOPDAPT 210

DAPT corto de 1 mes
- 0 a 1-mes: Aspirina + P2Y12
- Después de 1 mes: Monoterapia con clopidogrel

DAPT de 12 meses
- 0 a 1 mes: Aspirina + P2Y12
- 1 a 12 meses: Aspirina + Clopidogrel
- 12 a 60 meses: Monoterapia con aspirina

- Intervención coronaria percutánea (ICP) exitosa utilizando un stent liberador de everolimus de cobalto-cromo: XIENCE™
- Candidato para DAPT (aspirina/inhibidor del receptor P2Y12) durante 1 año

- Pacientes que necesitan anticoagulantes orales
- Historial de hemorragia intracraneal
- Complicaciones importantes en el hospital (IM/accidente cerebrovascular/hemorragia mayor)
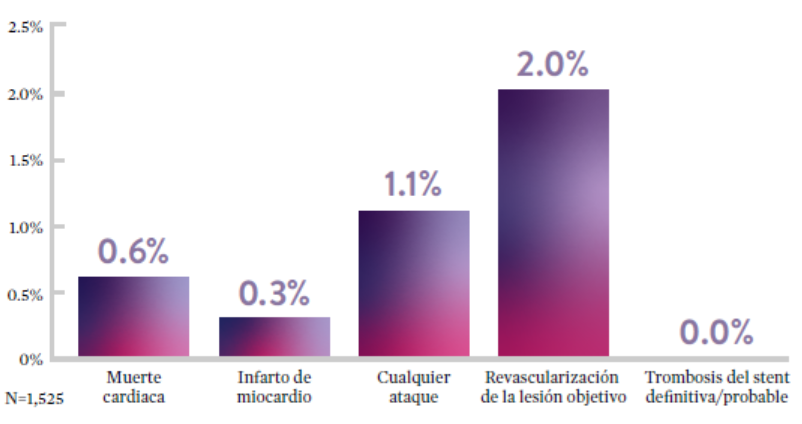
Ensayo STOPDAPT: La combinación del stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 3 meses es factible9
STOPDAPT9 fue el primer ensayo prospectivo que estudió la interrupción de la DAPT a los 3 meses después de la implantación. Entre otros resultados a 1 año, la tasa de trombosis de stent con XIENCE™ fue de 0.0%.
El ensayo STOPDAPT demuestra la factibilidad de usar el stent XIENCE™ con DAPT de 3 meses9

Conozca más acerca de STOPDAPT 2

“Vale la pena destacar que no se produjo ninguna trombosis de stent definitiva o probable en los pacientes tratados con XIENCE™ incluidos en STOPDAPT.”
— Masahiro Natsuaki, MD, Ensayo STOPDAPT9

STOPDAPT-3 Trial Design and Randomization11

- ICP con uso exclusivo y planificado de un stent liberador de everolimus (EES, por sus siglas en inglés ) de CoCr (XIENCE™)
- Presencia de paro cardíaco súbito (SCA, por sus siglas en inglés) o ARC-HBR
- Elegible para DAPT (aspirina/inhibidor P2Y12) durante 1 mes.
Diseño del estudio y aleatorización
Grupo 1:
0 a 1 mes: Aspirina + P2Y12 (Prasugrel)
Después de 1 mes: Monoterapia con clopidogrel
Grupo 2:
0 a 1 mes: P2Y12 (Prasugrel)
Después de 1 mes: Monoterapia con clopidogrel
El Ensayo STOPDAPT-311 se diseñó para estudiar la DAPT de 0 meses* (SAPT˄ utilizando solamente un inhibidor P2Y12) para pacientes con paro cardiaco súbito (SCA) y alto riesgo de sangrado (HBR).
Aunque los resultados son comparables tanto para hemorragias como para eventos isquémicos en los brazos de DAPT y TAPS, el estudio no cumplió con su criterio de valoración y concluyó en usar DAPT durante 1 mes después de la ICP.

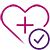
El stent XIENCE™ sigue siendo el ÚNICO DES con la indicación de DAPT más corta, que puede ser tan corta como 28 días.12


*As observed in the VACCAR trial (≥1.4 hours) and the PRO-PVI trial (≥1:26 time to ambulation) after successful close with Perclose device(s) in patients who have undergone cardiac arrhythmia treatments with multiple common femoral venous access sites.
**As observed in the PROFA trial (80% discharged within 3:34h) and the PRO-PVI trial (≥3:38 hours post-procedural time to discharge) after successful close with Perclose device(s) in patients who have undergone cardiac arrhythmia treatments with multiple common femoral venous access sites.
2. Mohammed et al (2022) Comparative outcomes of vascular access closure methods following atrial fibrillation. Vascular Closure for Cardiac Ablation Registry. (VACCAR) J Interv Card Electrophysiol 64, 301 -310
3. Castro-Urda et al (2023) Efficacy and safety of Proglide use and early discharge after atrial fibrillation (PROFA trial) Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 46(7), 598-606.
15. Mahadaven VS, et al. Pre-closure of femoral venous access sites used for large-sized sheath insertion with the Perclose device in adults undergoing cardiac intervention. Heart. 2008;94:571-572. doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2006.095935.
16. Sairaku A, et al. Rapid hemostasis at the femoral venous access site using a novel hemostatic pad containing kaolin after atrial fibrillation ablation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2011;31:157-164.
17. Verma S. Adopting a strategy of early ambulation and same-day discharge for atrial fibrillation ablation cases. EP Lab Digest. 2019;19(5).
18. Mercandetti M. Wound Healing and Repair. Medscape. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1298129-overview
19. Bhatt DL, et al. Successful “pre-closure" of 7Fr and 8Fr femoral arteriotomies with a 6Fr suture-based device (the Multicenter Interventional Closer Registry). Am J Cardiol. 2002;89:777-779.
20. Bartoletti S, Mann M, Gupta A, et al. Same‐day discharge in selected patients undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2019;42:1448-1455.
21. Deyell M, Macle L, Khairy P, et al. The efficacy of a same-day discharge protocol after atrial fibrillation ablation. Canadian J Cardiol. 2018;34:(10 suppl):S84. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2018.07.281.
22. Data on file at Abbott.
23. Verma, S., et al, Feasibility and Safety of Same Day Discharge for Patients Undergoing Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Ablation in a Community Hospital Setting. HRS 2020 Science Online, May 2020.
24. Sun, J. Y., et al. (2023). Feasibility and clinical benefits of the double-ProGlide technique for hemostasis after cryoballoon atrial fibrillation ablation with uninterrupted oral anticoagulants. Journal of geriatric cardiology : JGC, 20(4), 268–275.
25. Ahmed, A, Bawa, D, Kabra, R. et al. EFFICACY OF VENOUS CLOSURE METHODS AFTER ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCEDURES. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023 Mar, 81 (8_Supplement) 147.
26. Richard Tilz, R et al (2024) Venous Vascular Closure System Versus Manual Compression Following Single Shot Device AF Ablation -The STYLE-AF Study

MAT-XXXXXXX




